Circular Economy business models explained
We assume you already know what a circular economy is and want practical resources to innovate to reach a circular economy business model. For general circular economy resources, check out the Ellen MacArthur Foundation or the World Economic Forum.
What is a circular business model?
Circular business model definition
A circular business model articulates the logic of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value to its broader range of stakeholders while minimizing ecological and social costs.
Linear business models are based on the following logic: take natural resources, make products for consumers that eventually become waste. Circular business models contribute to a circular economy by adhering to the circular economy’s three fundamental principles.
- Design out waste and pollution
- Keep products and materials in use
- Regenerate natural systems
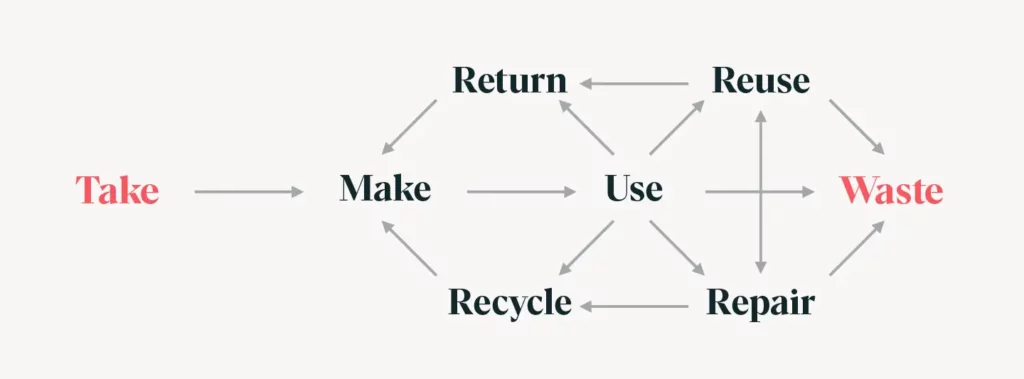
To better understand the relationship between a circular economy (the bigger picture) and circular business models (the smaller picture), it’s helpful to understand how businesses form a value chain. No singular business is the circular economy. That is to say, the circular economy is not one single vertically-integrated business.
Companies are like dots along the circle, forming a network between suppliers and customers called a value chain. This network can either be organized as a straight line between natural resources and landfills (linear economy) or creating a perpetual cycle of value with zero waste (circular economy).
How to create a circular business model?
1. Source products and materials from the economy, not from ecological reserves.
2. Create value for customers by adding value to existing products and materials.
3. Create valuable inputs for businesses beyond your customer.
Dive deeper into how we do circular business design.
What kind of circular business models are there?
- 1. Coordinating circular value chains through data: Creating products, from recycle to reuse.
- 2. Circular product design: Creating products, from recycle to reuse.
- 3. Use, reuse, share, and repair: Creating durable goods from recycled and reused parts can be inputs for downstream circular business models.
- 4. Collection & reverse logistics: Close the material life-cycle loop by creating products that can be upcycled, repurposed, and re-sold.
- 5. Sorting & preprocessing: Finding alternative value in the parts that make a product whole.
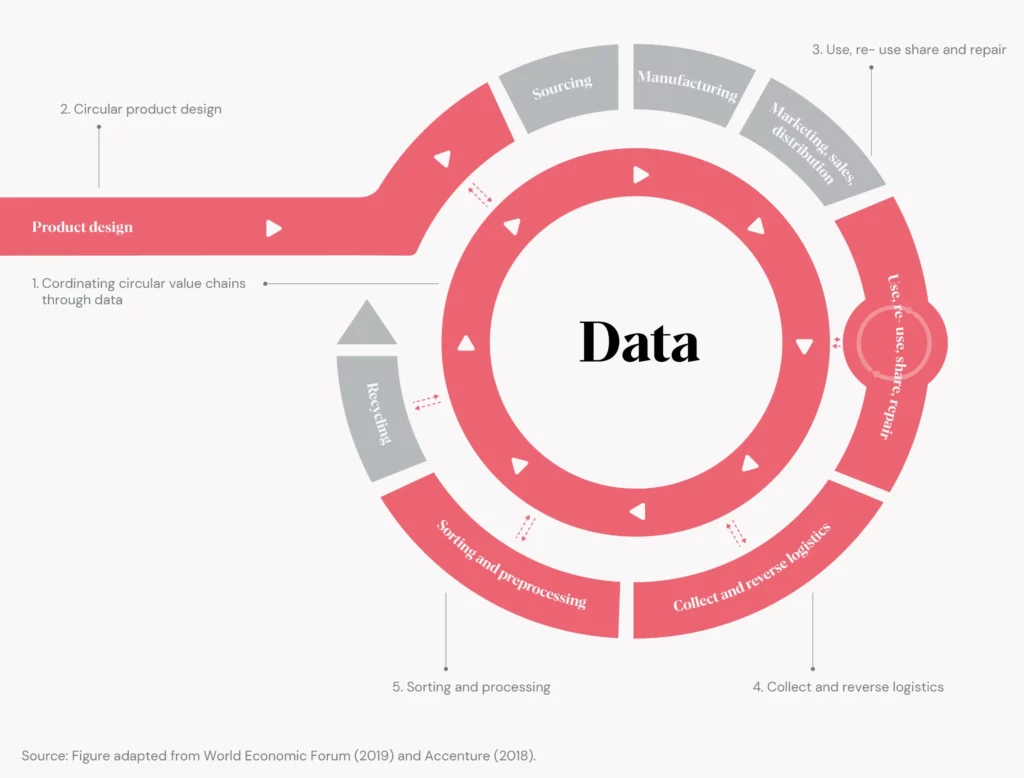
Circular economy business models come in all shapes and sizes, here are some examples we think are great.
Examples of how start-ups make money
Make a profit, while doing good for society with different business model ideas:
Default pricing: products with a mark-up
Subscription / rental revenue model
Platform-based business models
Intro to the Circular Economy, building better business models, define your strategy.