The headlines are looking pretty bleak. From income inequality and employee dissatisfaction to climate change – we have a lot of problems as a society. But thankfully, some companies are already bringing solutions to market.
Here, we highlight the organizations and institutions that are using the creative tools facilitated by business to tackle our biggest societal problems.
It features the latest and greatest innovations, broken up into the 4 social impact categories: community, equality, empowerment, and the environment. Read about the trends themselves in the next section, and then discover more details below.
Want to dive deeper into setting a responsible innovation strategy? Check our how we work with innovation strategy.
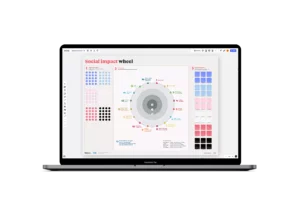
Is your innovation strategy socially responsible?
Put it to the test with our social impact wheel.
Equality innovations
- Promote equality across ethnicity, religion, gender, sexual orientation, and disability
- Promote equal job opportunities, fair reward system, and healthy work ethics
- Provide equal accessibility to offerings
Iceland & Finland
The pay disparity between men and women is often blamed on the breaks in employment women take to raise families. But the rise of paid paternity leave could reduce this drastically by enabling women to remain in the workforce while their partners care for their young children instead. By law, men and women in Iceland and Finland enjoy equal family leave. And some organizations are taking it upon themselves to offer generous paid paternity leave, including Facebook, Netflix, Spotify, and Etsy.
To encourage pay equality and lift the glass ceiling, the state of California will require all publicly traded companies to have at least 1 female minimum (and more depending on the number of people) on their board of directors by 2023.
How do local politicians interact with citizens? Town hall meetings often see the same few people attend, and reaching out to citizens directly can be expensive and time-consuming. Noticing that lawmakers were struggling to connect to their community, a digital citizen participation platform for governments called CitizensLab was developed. Based in Brussels, Belgium, CitizenLab gives “cities and governments a digital participation platform to consult their citizens on local topics and include them in decision-making.”
In some of the world’s poorest nations, many can’t afford traditional insurance premiums. So they’re left without a safety net when they want to start a business, etc. One solution is microinsurance – smaller premiums tailored to the unique needs of people living in poverty. We traveled to Rwanda to help four of the biggest local insurance companies come up with their very first microinsurance products for this target group.
Melinda Gates’s Pivotal Ventures has invested US$50 million into an initiative called Gender Equality in Tech (GET) Cities, the goal of which is to get more women into tech. They do so by partnering with organizations to encourage more female computer science graduates and by making tech hubs more female-friendly.
Unlike men, female salaries are often re-invested in the family rather than the stock market. But that can mean women are left in a worse financial position because the return from such investments doesn’t come in the form of cold hard cash. What’s more, 86% of investment advisors are men – so they have little chance of understanding ladies’ unique financial priorities. Using design thinking principles, digital investment platform Ellevest is tackling this problem by offering female-first financial strategies tailored to women’s salaries, and longer lifespan.
Using artificial light to encourage food growth is nothing new, but it is scaling up rapidly. This technology – which uses light at specific wavelengths to help plants grow without the sun – could enable those in extreme climates to access fruits and vegetables.
The PaperWeight Armband is a tool that can identify malnutrition in a non-invasive way. Not only will this help healthcare workers, carers, and volunteers diagnose the problem, but it will enable more communication by enabling sufferers to see the evidence for themselves. This will be handy for both the elderly and people in developing nations.
Virtual reality is geared towards men. Why? Virtual reality sickness. Yes, it’s a thing, and it impacts more women than men. Researchers aren’t sure why, but one reason could be that most headsets are designed for men. VR headsets need to be adjusted to the distance between the pupils of the user’s eyes – which is often shorter for women. The default setting of the headsets offered now is often greater than the interpupillary distance of a woman’s eyes. Tackling this problem could encourage adoption among female user groups, enabling women to employ this technology comfortably for gaming, a range of training purposes – who knows? This is a major female-centered design opportunity.
Unlock the power of AI in a unique sprint format. Leverage the latest AI tools to generate new ideas, get real-time feedback, and curate new concepts to move forward with.
Community innovations
- Encourage employee self-development and contribution
- Support the mental and physical health of employees
- Build collaborative partnerships
Last year, the world’s first 3D-printed neighborhood began construction in Mexico. Built in the region of Tabasco, the houses were designed to withstand earthquakes and replace homes that poorer residents built themselves out of metal, wood, and anything else they could afford.
Squirrel AI Learning is an adaptive learning platform in China. The platform’s goal is to give students in high school and below personalized AI tutoring. The pricing structure is reasonable, enabling poorer students to access personalized support.
Teacherly aims to help teachers across the globe improve their teaching skills and share knowledge. It facilitates the sharing of best practices, learning outcomes, and professional development materials. It also enables them to plan lessons together and get support, feedback, and advice.
Last year, Atlanta’s city council purchased the largest edible forest in the USA. Covering 7 acres, it contains more than 100 fruit and nut trees for local residents to pick food and grow their own via a range of planter boxes. Initiatives like this can help provide affordable fruits and vegetables to people living below the poverty line. The city aims to ensure 86% of its residents live within half a mile of a fresh food source by 2021.
Last year, plant-based seafood producer Sophie’s Kitchen won The Liveability Challenge – a competition searching for ideas to improve the lives of people in Southeast Asia – by developing a protein made from microalgae. Available for US$2 per kilogram and requiring just 0.02 hectares of land to produce, it can be used to improve nutrition via supplements, cooking oil, and more.
Desert Control
Norwegian company Desert Control has developed a concoction that can be sprayed on the sand in deserts to enable it to hold water and grow crops. They spray a mixture of water and clay, called liquid nano clay, just half a meter deep into the sand to achieve this result. This technology could facilitate food production in poorer climates and combat desertification.
A paper published in the scientific journal Chem reveals that researchers have uncovered a material which can nullify disease-causing bacteria in water. Using sunlight and a photocatalyst, it works like a magnet to clean water and ensure that no harmful bacteria or pollutants remain.
Empowerment innovations
- Encourage employee self-development and contribution
- Support the mental and physical health of employees
- Build collaborative partnerships
Waggl is a feedback platform that lets managers, administrators, and employees share their sentiments in real-time. It gets people engaged and encourages actionable dialogue around topics that matter in the workplace.
Uman AI is a collaboration platform for teams that thrive on knowledge. It gathers company knowledge and helps people proactively teach themselves new skills.
Limeade is an interactive platform for employees that aims to improve the employee experience. To support them in their daily lives and boost their sense of purpose and wellbeing, it brings trainings, engagement tools, communication solutions, access to mentorship, and more to the employee’s mobile phone. The platform may encourage open dialogue in large organizations.
Microsoft Japan made headlines when it introduced a 4-day work week, and the move has also delivered results. Productivity jumped by 40%.
Socially responsible investing (SRI) involves avoiding companies that sell addictive or abusive substances (like alcohol, tobacco, etc.) and those that have a negative impact on society in favor of businesses championing low carbon exposure, cleantech, gender diversity, etc. Robo SRI platforms like Wealthsimple empower consumers to put their money where their mouth is when it comes to their social footprint.
Triodos is a bank that only lends money to organizations that can prove they’re having a positive impact on society and the environment. They also aim to be more transparent and open about their charges to make banking more honest.
Environment innovations
- Responsible consumption of natural resources, including clean energy
- Regenerative business model: No waste and circularity of resources
- Provide a safe and clean work environment
Students studying civil engineering at the University of the Philippines created a concrete alternative from glass, fly ash, a common rock found on campus, and other recycled materials. Tests confirmed that the concrete alternative was comparably strong and durable, while it performed better than traditional concrete – made from cement, gravel, and water – on the environmental scale.
Heliogen is a solar power company that uses AI to concentrate and capture more sunlight than traditionally possible. Doing so enables them to produce “carbon-free, ultra-high temperature (up to 1500ºC) heat” for use in heavy industry (cement, steel, etc.) – which accounts for more than a fifth of all global greenhouse gas emissions.
Fake sunflowers
Biomimicry at its finest, researchers at the University of California have developed artificial sunflowers. Known as SUNbots, these fake sunflowers are less than 1 millimeter in diameter are made of materials that react to heat in order to bend towards sunlight and harvest more power. This tech could make solar power more efficient.
Altered company has created a new type of nozzle that reduces water usage by up to 98%. Attach the nozzle – which rotates at high speeds – to any tap, and it will turn the water produced into a heavy mist, which increases the surface area of the water without sacrificing pressure, they say.
Microsoft
Like IKEA, Microsoft has pledged to become a carbon negative organization. By 2030, Microsoft intends to make up for all the carbon emissions it’s produced throughout its existence.
UK supermarket Marks & Spencer has partnered with vertical-farming-unit supplier Infarm to grow herbs in-store. Urban farming opens up a range of possibilities for the environment, from reducing emissions by eliminating transport from farms to cities, to eliminating CO2 from the air.
Regenerative agriculture – which involves establishing farming, fishing, and grazing practices that are sustainable – is becoming more mainstream. Regrarians is a company that educates farmers and designs farm plans to enable them to adopt regenerative agricultural practices.
WildTrack
WildTrack uses AI to analyze animal footprints. By reviewing the tracks, this technique can determine the species (of an individual rhino, for instance), age-class, and sex based on measurements of the anatomical points (‘landmark points’). This is fantastic news as it enables them to monitor endangered species in a non-invasive way.
Firemap is a tool that uses data-driven predictive modeling to identify areas at high risk of wildfires and track existing ones. Through it, you can quickly access information on past fires and check the current situation and weather forecast based on satellite detection, as well as information on vegetation and landscapes.
20tree.AI uses various details to identify areas at high risk of wildfires to help governments prevent them and take the necessary steps to minimize the environmental impact when they do occur.
Electric cars are fairly quiet, which means pedestrians can’t hear them coming. To reduce the risk, the US and EU will soon require electric cars to emit a sound when driving at low speeds. But what sound should these cars make? Well, an independent Toyota manufacturer and distributor in Uruguay called Ayax has an ingenious solution. Ayax has developed an artificial sound for electric cars that plays at the right bandwidth and frequency to help plants grow. Initial tests show it works.
Sweden
Sweden built a road that charges electric cars while they drive. The roads have an electric rail embedded in them, and e-vehicles can charge their batteries by lowering a movable arm attached to the bottom of the car. The roads are safe to walk on as the electricity is below the surface.
London startup Abornea’s BioSolar Leaf panels grow edible algae to produce food ingredients while reducing CO2 levels. This technology can be used as a means to minimize CO2 around cities as the panels take up minimal space. The algae grown on a single solar panel absorbs as much CO2 as 100 trees per day.
IFIXIT is trying to help us veer away from the disposable product trend by pushing for our ‘right to fix’ products. This is to benefit not only the environment but also our wallets. They do so by sharing online repair guides and resources to help people fix or modify everything from computers, to phones, vehicles, and home appliances. At last count, they’d listed around 54,000 manuals.
Dutch airline KLM and Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) are designing a new aircraft that uses up to 20% less fuel than the AirbusA350. Their proposed lightweight design, called the ‘Flying-V,’ will make the passenger seating and engines part of the wings. “Our ultimate aim is one of emission-free flight,” explains Henri Werij, dean of the Faculty of Aerospace Engineering at TU Delft.
Harbour Air managed to create a 6-seater e-plane and fly it for 15 minutes. Though not very useful just yet, this development is a step in the right reduced-emissions-air-travel direction.
W Hotels partnered with clothing rental company Rent The Runway to offer a ‘Closet Concierge’ service – so guests can have their rented clothing delivered directly to their rooms. This could enable travelers to pack less, which could reduce the weight on flights and save on fuel.
Stanford researchers have developed a detailed roadmap to tackle the climate crisis worldwide. Their outline – which many say is, in fact, conservative – goes into detail about how 143 countries can transition to 100% renewable energy by 2050 using an investment of US$73 trillion.
The Great Bubble Barrier is a process that can divert 80% of plastic rubbish to the side of rivers before it has a chance to reach the ocean. How? With air. The system pumps air via a device laid diagonally on the riverbed. The bubbles produced push the rubbish to the side of the river for collection. This process is less harmful to wildlife than physical barriers.
Turbulent makes small, cost-efficient turbines that can be installed in rivers and streams (that have minimal height differences) to generate power. This technology can be used to supply homes and small villages with an independent, continuous energy supply.
Clever people at Hong Kong University have found a way to repurpose the heat produced by computers, ovens, and aircon exhausts. They’ve developed a cheap, adjustable energy recycling cell that can convert this excess heat into electricity for repeat use.environment-
McDonald’s X Ford
Ford and McDonalds are working together to bioengineer car parts from coffee grounds. Not only will they repurpose food waste, but the parts will use less petroleum and be lighter than traditional car parts.
UK company Dendra Systems has found a way to plant trees 150 times faster with the help of drones. The drones quickly and accurately shoot biodegradable pods into the ground. Dendra Systems hopes to plant 500 billion trees.
Malaysian enterprise Green Hope has found a way to create biodegradable bags from cassava trees. While there are a lot of biodegradable materials around of late, this innovation is exciting because the bags – created using the starch in the roots of cassava trees (grown in Indonesia) – aren’t made from edible materials. So production won’t disrupt food chains.
JD.com is helping people in Shanghai, China, meet waste management requirements. People can upload a picture of their trash to JD.com’s app, and its AI program will tell them whether the waste is recyclable, wet, dry, or hazardous.
UK-based Teemill is a circular clothing company that makes t-shirts out of second-hand clothing and recycles its old tees when their best years are over. Oh, and the whole process is powered by renewable energy.
Last year, France banned the destruction of unsold consumer goods – a wasteful practice that saw up to $900 million in products destroyed each year. By 2023, brands will have to donate, reuse, or recycle everything they make.
Wrangler is dying its denim with foam, which uses much less water than the traditional process.
Food waste is a big issue all over the world. But in China, cockroaches are sorting through it. See, they’re not all bad! In one cockroach farm in Jinan, China, a billion cockroaches chew through 45 tonnes of the stuff each day. They’re also used as a ground-up food source for livestock.

Is your innovation strategy socially responsible?
Put it to the test with our social impact wheel.


